If dystrophy of the peripheral zone with damage of the choroid and retina is detected, the ophthalmologist will diagnose chorioretinal dystrophy. If characteristic damage is also found in the vitreous body - vitreochorioretinal dystrophy.
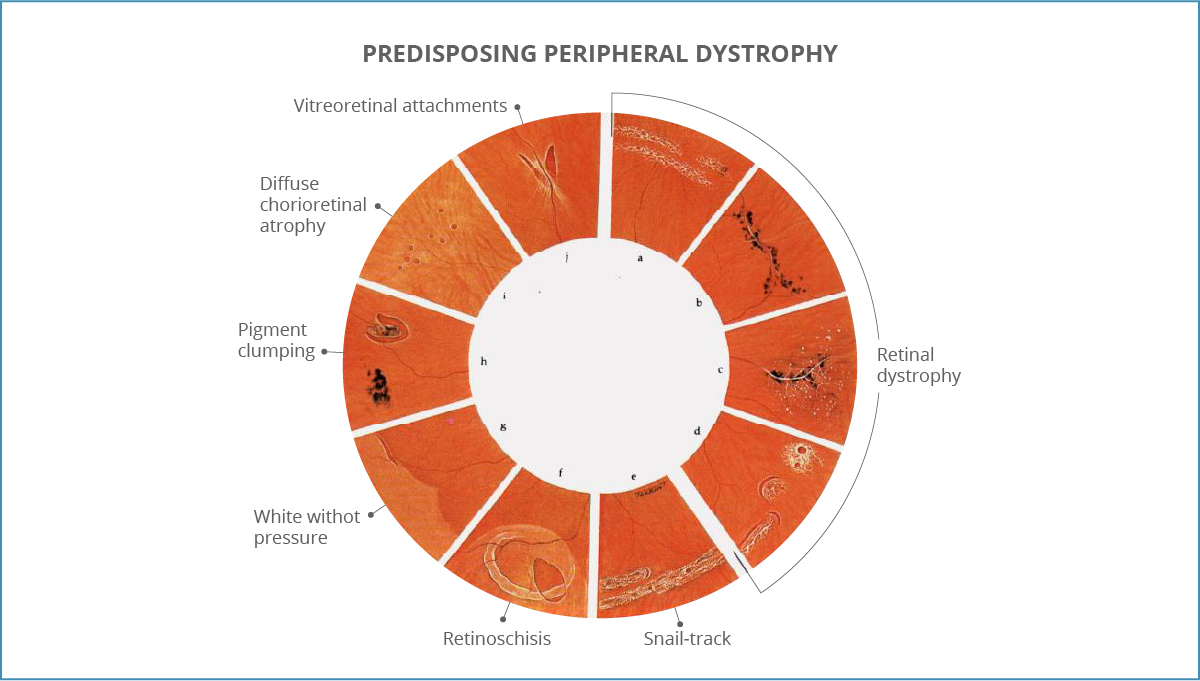
Asymptomaticity is the main problem of peripheral retinal dystrophy, the progress of which is not felt by a person.
The second problem of the disease is the difficulty in diagnosing it, especially in the early stages of the process. The main factor in the successful detection of dystrophy is the appropriate qualifications of the specialist and the use of the latest generation equipment.
During the initial diagnosis, a study of the peripheral area is carried out by dilating the pupil to the maximum possible size and examining it using a three-mirror instrument - the “Goldmann lens”. Additionally, visual fields are checked, and some other examinations are carried out.
It is impossible to completely cure this disease and restore damaged areas of the eye.
If there are breaks, further retinal detachment can be prevented with laser coagulation.
Additionally, regular ophthalmological examinations are recommended.